
Sometimes, they stop sending electrical signals completely. If it gets damaged, your nerves can’t send electrical signals as quickly. The myelin sheath is like the insulation around electrical wiring. Myelin surrounds the axons in a layered sheath (coating). Outside of your central nervous system (brain and spinal cord), cells called Schwann cells surround the axons.īoth oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells contain a fatty tissue called myelin. In your brain, cells called oligodendrocytes surround axons.
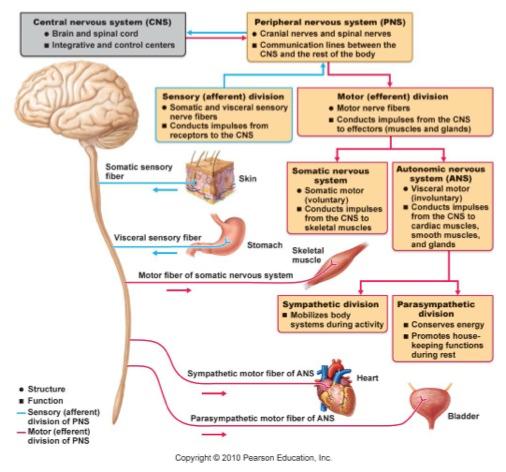
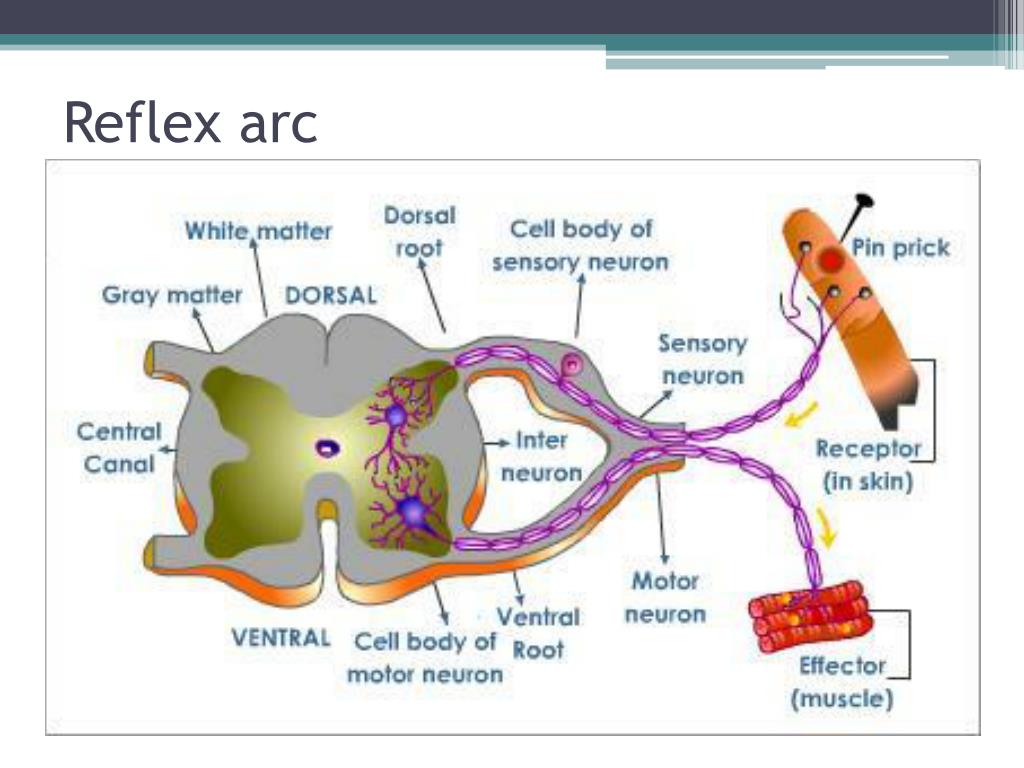
The neurotransmitter binds to a receptor on the muscle or connecting neuron and converts to another electrical signal.The chemical releases molecules called neurotransmitters, into a space that bridges the space between one neuron to another.The message converts to a chemical signal at the end of the nerve called the axon hillock.The signal travels down the axon, the “wiring” connection of the nerve.When a nerve sends an electrical impulse: Some reactions are reflexive, happening below the level of consciousness, like moving your hand away from a hot stove. Your brain integrates these messages (inputs) to inform everything you do, including how you move, feel, behave and think. It receives and interprets nerve signals from your peripheral nervous system. Your central nervous system is your brain and spinal cord.Your peripheral nervous system is the network of nerves that transmit (carry) signals from all over your body to your spinal cord, which is part of your central nervous system.Your nerves help the two parts of your nervous system communicate with each other: How do nerves function with the rest of the nervous system? Senses (touch, pain, feeling hot or cold, vibration, hearing, sense of balance, taste, smell and sight).Nerves send electrical signals from one part of your body to another. Spinal nerves also control some of your reflexes or involuntary responses, such as pulling your hand away from a hot stove. For example, spinal nerves may carry sensations from your joints and muscles to your spinal cord. These nerves can provide sensory function, motor function or both. Spinal nerves: You have 31 pairs of spinal nerves branching out from your spinal cord.For example, cranial nerves help you make facial expressions, move your eyes and process smells. Cranial nerves can have sensory functions, motor functions or both. Cranial nerves : These 12 nerve pairs originate in your brain and extend through your face, head and neck.You also have two main groups of nerves branching out from your brain and spinal cord: Motor nerves carry signals to your muscles or glands to help you move and function.Sensory nerves carry signals to your brain to help you touch, taste, smell and see.This is called your peripheral nervous system. Most of the time when doctors use the term “nerve,” they’re referring to the part of your nervous system outside of your brain and spinal cord. Nerves, together with your brain and spinal cord, are the foundation of your nervous system. Neurons are present all over your body, especially in your brain and spinal cord. They also maintain certain autonomic functions like breathing, sweating or digesting food. These impulses help you feel sensations and move your muscles. Nerves are like cables that carry electrical impulses between your brain and the rest of your body.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
